 The Summarize Within tool calculates statistics in areas where an input layer overlaps a boundary layer.
The Summarize Within tool calculates statistics in areas where an input layer overlaps a boundary layer.
Workflow diagram
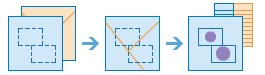
Examples
A city is trying to deal with a backlog of maintenance projects and wants to involve the maintenance assessment districts in projects related to streetlight and bike route maintenance. The Summarize Within tool is used to count the number of streetlights and miles of bike routes in each district so that the projects can be prioritized effectively.
A cable provider is starting a pilot program where it provides low-cost Internet access to low-income community college students. Summarize Within will be used to determine the number of low-income families in each college district so the cable provider can choose an appropriate district for its pilot program.
A development company is looking to make some money by creating a new mixed-use development in an urban center. Summarize Within can be used to summarize the qualifying zones within the city's boundary to find the total area of potential development zones.
Usage notes
The inputs for Summarize Within include one area layer that serves as the boundary for summarizing features and a point, line, or area layer to be summarized.
You can provide the area layer to use for analysis, or you can generate bins of a specified size and shape (hexagon or square) into which to aggregate. The bin size specifies how large the bins are. If you are aggregating into hexagons, the size is the height of each hexagon and the width of the resulting hexagon will be 2 times the height divided by the square root of 3. If you are aggregating into squares, the bin size is the height of the square, which is equal to the width.

Tip:
You can add a layer that is not in Map Viewer to the tool pane by selecting Choose Analysis Layer in the drop down menu.
A Count of Points, Total Length, or Total Area box will appear depending on the type of features to summarize in your layer. The boxes are checked by default and can only be unchecked if statistics are being calculated. The default distance measure will depend on the Units in your profile.
| Total | Input Features | Default | Options |
|---|---|---|---|
Count of Points | Points | None | None |
Total Length | Lines | Miles (U.S. Standard setting) or Kilometers (Metric setting) |
|
Total Area | Areas | Square Miles (U.S. Standard setting) or Square Kilometers (Metric setting) |
|
There are five options for statistics that can be calculated on numeric fields in the layer to be summarized: sum, minimum, maximum, average, and standard deviation. Each time a Field and Statistic is entered, a new row will be added to the tool pane so more than one statistic can be calculated at once. The summarized data can be viewed in the result layer's table or pop-ups.
Optionally, a group by field can be selected so statistics are calculated separately for each unique attribute value. When a group by field is selected, the pop-up for each of the features in the output layer will contain charts showing each summary count or total and statistic by field value. A summary table listing each feature and statistic by group by field value will also be created.
The Add minority, majority and Add percentages boxes are enabled when a group by field is entered. The minority and majority will be the least and most dominant value from the group by field, respectively, where dominance is determined using the count of points, total length, or total area of each value. When Add minority, majority is checked, two new fields will be added to the result layer. The fields will list the values from the group field that are the minority and majority for each result feature. When Add percentages is checked, two new fields will be added to the result layer listing the percentage of the count of points, total length, or total area that belong to the minority and majority values for each feature. A percentage field will also be added to the result table listing the percentage of the count of points, total length, or total area that belong to all values from the group by field for each feature.
If Use current map extent is checked, only those features in the input layer and the layer to be summarized that are visible within the current map extent will be analyzed. If unchecked, all features in both the input layer and the layer to be summarized will be analyzed, even if they are outside the current map extent.
Limitations
- The boundary input must be area features.
- Lines and areas are summarized using proportions; therefore, it is best to summarize absolute data (such as population) rather than relative data (such as average income) when lines or areas are being summarized.
- There is no option to remove boundaries that do not overlap any point, lines, or areas.
How Summarize Within works
Generating bins
Square and hexagonal bins can be generated for aggregation areas rather than summarizing features into an input area layer. The bins are generated in a custom, area-preserving projected coordinate system using the specified size dimensions to ensure the sizes are equal and appropriate for the area of interest. An appropriate equal-area projection and parameters are chosen based on the geographic extent of the input layers. Once bins are created, they are projected back to the coordinate system of the input data before being used in the analysis.
After the analysis is complete, the result is projected to Web Mercator for display (the default) or to the projection of your custom basemap. A Web Mercator projection may cause your results to appear distorted, especially for large bins or bins near the polar regions. These distortions are part of the display only and do not reflect an inaccurate analysis.
Equations
Average and Std Deviation are calculated using weighted mean and weighted standard deviation for line and area features. None of the statistics for point features are weighted. The following table shows the equations used to calculate standard deviation, weighted mean, and weighted standard deviation.
| Statistic | Equation | Variables | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
Standard Deviation | 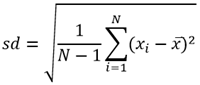 |  | Points |
Weighted Mean | 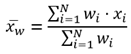 |
| Lines and Areas |
Weighted Standard Deviation | 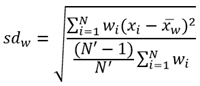 |
| Lines and Areas |
Points
Point layers are summarized using only the point features within the input boundary. The results will be displayed using graduated symbols.
The figure and table below explain the statistical calculations of a point layer within a hypothetical boundary. The Population field was used to calculate the statistics (Sum, Minimum, Maximum, Average, and Std Deviation) for the layer.
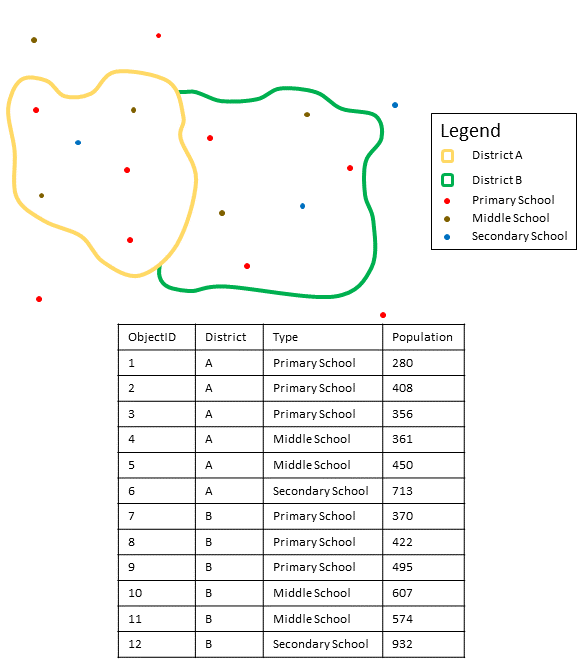
| Statistic | Results District A |
|---|---|
Sum | |
Minimum | Minimum of: |
Maximum | Maximum of: |
Average | |
Std Deviation | 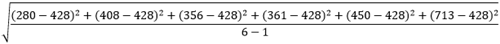 |
A real-life scenario in which this analysis could be used is in determining the total number of students in each school district. Each point represents a school. The Type field gives the type of school (elementary, middle school, or secondary) and a student population field gives the number of students enrolled at each school. The calculations and results are given for District A in the table above. From the results you can see that District A has 2,568 students. When running the Summarize Within tool, the results would also be given for District B.
Lines
Line layers are summarized using only the proportions of the line features that are within the input boundary. When summarizing lines, use fields with counts and amounts rather than rates or ratios so proportional calculations make logical sense in your analysis. The results will be displayed using graduated symbols.
The figure and table below explain the statistical calculations of a line layer within a hypothetical boundary. The Volume field was used to calculate the statistics (Sum, Minimum, Maximum, Average, and Std Deviation) for the layer. The statistics are calculated using only the proportion of the lines that are within the boundary.
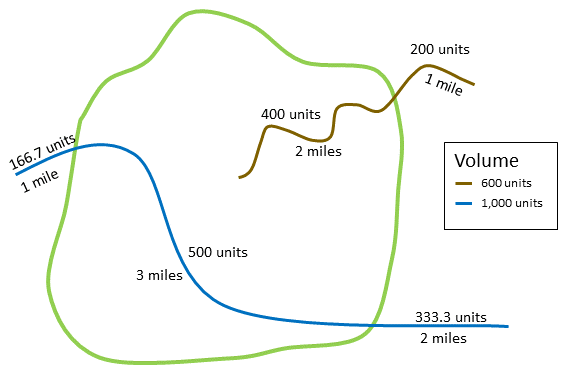
| Statistic | Result |
|---|---|
Sum | |
Minimum | Minimum of: |
Maximum | Maximum of: |
Average | 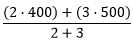 |
Std Deviation | 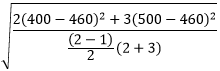 |
A real-life scenario in which this analysis could be used is in determining the total volume of water in rivers within the boundaries of a state park. Each line represents a river that is partially located inside the park. From the results, you can see that there are 5 miles of rivers within the park and the total volume is 900 units.
Areas
Area layers are summarized using only the proportions of the area features that are within the input boundary. When summarizing areas, use fields with counts and amounts rather than rates or ratios so proportional calculations make logical sense in your analysis. The results layer will be displayed using graduated colors.
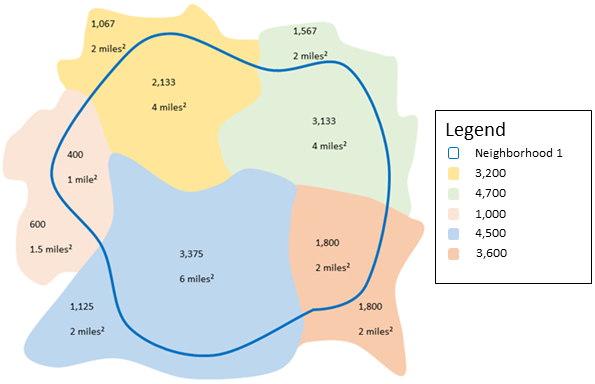
The figure and table below explain the statistical calculations of an area layer within a hypothetical boundary. The populations were used to calculate the statistics (Sum, Minimum, Maximum, Average, and Std Deviation) for the layer. The statistics are calculated using only the proportion of the area that is within the boundary.
| Statistic | Result |
|---|---|
Sum | |
Minimum | Minimum of: |
Maximum | Maximum of: |
Average | 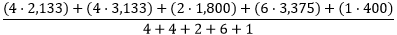 |
Std Deviation | 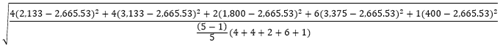 |
A real-life scenario in which this analysis could be used is in determining the population in a city neighborhood. The blue outline represents the boundary of the neighborhood and the smaller areas represent census blocks. From the results, you can see that there are 10,841 people in the neighborhood and an average of approximately 2,666 people per census block.
Similar tools
Use Summarize Within to calculate statistics for features that overlap a boundary layer. Other tools may be useful in solving similar but slightly different problems.
Map Viewer analysis tools
If you are trying to summarize points and only want to keep the boundaries with a count greater than zero, use the Aggregate Points tool.
If you are trying to summarize features within a distance of your input features, use the Summarize Nearby tool.
ArcGIS Pro analysis tools
Summarize Within performs the functions of the Spatial Join and Summary Statistics tools.
Summarize Within is also available in ArcGIS Pro. To run the tool from ArcGIS Pro, your project's active portal must be running Portal for ArcGIS 10.5 or later. You must also sign in to the portal using an account that has privileges to perform standard feature analysis in the portal.

