ArcGIS Data Store is part of the overall ArcGIS Enterprise platform.
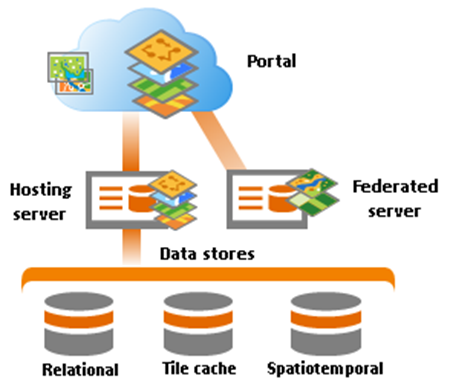
There are three ArcGIS Data Store types you can use: relational, tile cache, and spatiotemporal big data stores. All three store data for services that run on the ArcGIS GIS Server site that you configure as your Enterprise portal's hosting server.
The following table lists which type of service uses each type of data store:
| Layer/service type | Type data store used |
|---|---|
Hosted feature layers (feature services) published to the Enterprise portal from ArcGIS Pro, ArcMap, or in the portal website | Relational data store |
Hosted feature layers (feature services) created as output from standard feature analysis tools in Map Viewer or Insights for ArcGIS | Relational data store |
Hosted spatiotemporal feature layers (feature services) created as output from GeoAnalytics Tools in Map Viewer or ArcGIS Pro | Spatiotemporal big data store |
Feature layers (feature services) created to archive real-time data from a federated ArcGIS GeoEvent Server | Spatiotemporal big data store |
The tracking service used for location tracking (Tracker for ArcGIS) | Spatiotemporal big data store |
Hosted scene layers (scene services) published to the Enterprise portal | Tile cache data store |
For best performance, each of these data stores should run on a different machine; otherwise, they will contend for memory resources.
Since ArcGIS Server, Portal for ArcGIS, and ArcGIS Data Store all work together, you must have the following to configure and use ArcGIS Data Store:
- At least one GIS Server site that can communicate over HTTPS
- An Enterprise portal to which you can add a hosting server and federated servers
Install and configure a GIS Server site
The GIS Server site you use as the portal's hosting server must be installed and configured before you create any data stores. Follow the instructions in the ArcGIS Server installation guide to install and configure a GIS Server site.
Esri recommends that your data stores run on different machines than your ArcGIS Server sites so they don't compete for memory and other resources. This is especially important for spatiotemporal big data stores; you should always install those on their own machines separate from other software such as ArcGIS Server and other data stores.
License:
An exception to this is if you are configuring workgroup ArcGIS Enterprise deployment, which would not be used by as many clients. See the ArcGIS Enterprise functionality matrix for an overview and your Esri license agreement for full details on configuration restrictions.
ArcGIS Data Store, Portal for ArcGIS, and ArcGIS Server all communicate over HTTPS by default. If you change the HTTP protocol settings for any of these components, be sure they can all still communicate with one another. In other words, do not change one of the components to communicate over HTTP only and leave the others set to communicate over HTTPS only.
Once the GIS Server site you will use for your hosting server exists, you can create the data stores you need. Before you start using the system, you need to install and configure Portal for ArcGIS, and register federated servers and a hosting server.
Install and configure Portal for ArcGIS
If you have not already done so, set up your portal. See Getting started with Portal for ArcGIS for instructions.
As mentioned in the previous section, it is best to install Portal for ArcGIS on a machine separate from your data stores, especially in the case of spatiotemporal big data stores.
Once your portal exists, the portal administrator can federate servers and designate a hosting server. See Federate an ArcGIS Server site with your portal and Configure a hosting server for instructions.
For portal members to use the functionality that writes to each type of ArcGIS Data Store, the portal administrator must assign members to roles that have the required privileges. For information on portal privileges and assigning roles, see User types, roles, and privileges and Configure roles.